第1章 索引介绍
1.介绍
索引相当于⼀本书的⽬录,可以优化查询。
2.索引查找算法
1 --> 100 盒⼦
谁最快猜到数字,礼品归谁。
我会给⼤家提示。
1. 遍历
2. ⼆分法 ---> ⼆叉树 ---> 红⿊树 ---> Balance Ttree(平衡多叉树,简称为
BTREE)
3.BTREE查找算法演变
1.B-TREE : 普通 BTREE
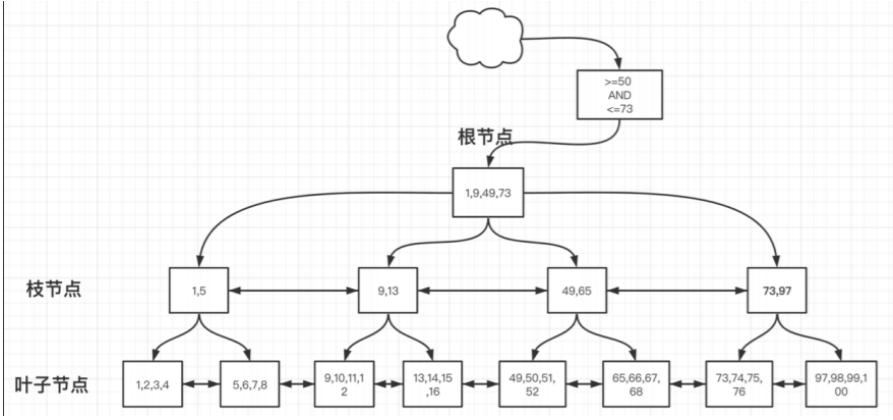
2.B+TREE : 叶⼦节点双向指针
3.B++TREE(B*TREE):枝节点的双向指针
B-TREE示意图:
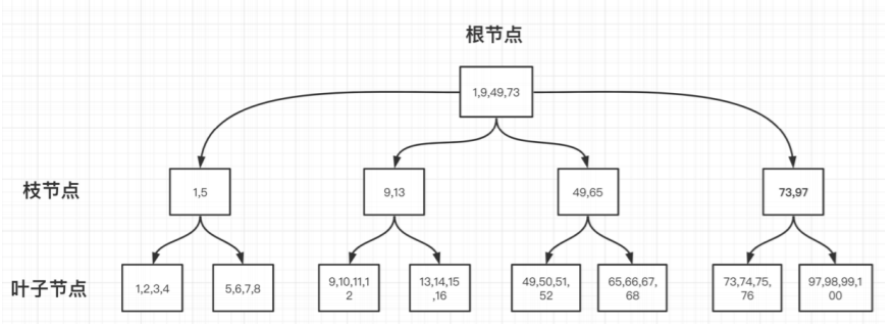
B++TREE示意图:
第2章 聚簇(区)索引
1.前提
1.如果表中设置了主键(例如ID列),⾃动根据ID列⽣成索引树。
2.如果没有设置主键,⾃动选择第⼀个唯⼀键的列作为聚簇索引
3.⾃动⽣成隐藏的聚簇索引
2.建议
在建表时,显示的创建主键,最好是数字⾃增列
3.功能
1.录⼊数据时,按照聚簇索引组织存储数据,在磁盘上有序存储数据⾏。
2.加速查询。基于ID作为条件的判断查询。
4.构建过程
1.叶⼦节点: 存储数据⾏时就是有序的,直接将数据⾏的page作为叶⼦节点(相邻的叶⼦结点,有双向指针)
2.枝节点: 提取叶⼦节点ID的范围+指针,构建枝节点(相邻枝节点,有双向指针)
3.根节点: 提取枝节点的ID的范围+指针,构建根节点
第3章 辅助索引
1.前提
需要⼈为创建辅助索引,将经常作为查询条件的列创建辅助索引,起到加速查询的效果。
2.功能
按照辅助索引列,作为查询条件时。
1.查找辅助索引树,得到ID值
2.拿着ID值回表(聚簇索引)查询
3.构建过程
1.叶⼦节点:提取主键(ID)+辅助索引列,按照辅助索引列进⾏从⼩到⼤排序后,⽣成叶⼦节点。(相邻的叶⼦结点,有双向指针)
2.枝节点 :提取叶⼦节点辅助索引列的范围+指针,构建枝节点(相邻枝节点,有双向指针)
3.根节点 :提取枝节点的辅助索引列的范围+指针,构建根节点
第4章 索引考虑事项
1.回表是什么? 回表会带来什么问题? 怎么减少回表?
a. 按照辅助索引列,作为查询条件时,先查找辅助索引树,再到聚簇索引树查找数据⾏的过程。
b. IO量多、IO次数多、随机IO会增多
减少回表:
1. 辅助索引能够完全覆盖查询结果,可以使⽤联合索引。
2. 尽量让查询条件精细化,尽量使⽤唯⼀值多的列作为查询条件
3. 优化器:MRR(Multi-Range-Read), 锦上添花的功能。
mysql> select @@optimizer_switch;
mysql> set global optimizer_switch='mrr=on';
功能:
1. 辅助索引查找后得到ID值,进⾏⾃动排序
2. ⼀次性回表,很有可能受到B+TREE中的双向指针的优化查找
2.索引树⾼度的影响因素? 如何解决?
a. ⾼度越低越好
b. 数据⾏越多,⾼度越⾼。
1. 分区表。⼀个实例⾥管理。
2. 按照数据特点,进⾏归档表。
3. 分布式架构。针对海量数据、⾼并发业务主流⽅案。
4. 在设计⽅⾯,满⾜三⼤范式。
c. 主键规划:⻓度过⻓。
1. 主键,尽量使⽤⾃增数字列。
d. 列值⻓度越⻓,数据量⼤的话,会影响到⾼度。
1. 使⽤前缀索引
100字符 只取前10个字符,构建索引树
e. 数据类型的选择。
选择合适的、简短的数据类性。
例如:
1. 存储⼈的年龄 ,使⽤ tinyint 和 char(3)哪个好⼀些
2. 存储⼈名,char(20)和varchar(20)的选择哪⼀个好。
a. 站在数据插⼊性能⻆度思考,应该选:char
b. 从节省空间⻆度思考,应该选:varchar
c. 从索引树⾼度的⻆度思考,应该选:varchar
建议使⽤varchar类型存储变⻓列值。
第5章 索引应⽤
1.压测
source /root/t100w.sql
mysqlslap --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --concurrency=100 --iterations=1
--create-schema='test' --query="select * from test.t100w where
k2='780P'" engine=innodb --number-of-queries=2000 -uroot -p123 -verbose
--concurrency=100 : 模拟同时100会话连接
--create-schema='test' : 操作的库是谁
--query="select * from test.t100w where k2='780P'" :做了什么操作
--number-of-queries=2000 : ⼀共做了多少次查询
Running for engine rbose
Average number of seconds to run all queries: 648.657 seconds
Minimum number of seconds to run all queries: 648.657 seconds
Maximum number of seconds to run all queries: 648.657 seconds
Number of clients running queries: 100
Average number of queries per client: 20
2.查询表的索引
查看索引:
desc t100w;
show index from t100w;
索引类型:
-----
Key
-----
PK --> 主键(聚簇索引)
MUL --> 辅助索引
UK --> 唯⼀索引
3.创建索引
3.1 单列辅助索引
查询语句:
select * from test.t100w where k2='780P'
优化⽅法:
alter table 表名 add index 索引名(列名);
alter table t100w add index idx_k2(k2);
3.2 创建联合索引
mysql> alter table t100w add index idx_k1_num(k1,num);
3.3 前缀索引创建
select count(distinct(left(name,5))) from city ;
select count(distinct name) from city ;
创建前缀索引
mysql> alter table city add index idx_n(name(5));
4.删除索引
alter table city drop index idx_n;
第6章 执⾏计划获取和分析
1.命令介绍
explain
desc
2.使⽤⽅法
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN';
mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode='CHN';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------
-----+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key
| key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------
-----+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | city | NULL | ref | CountryCode |
CountryCode | 3 | const | 363 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------
-----+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
3.执⾏计划信息介绍
table :此次查询访问的表
type :索引查询的类型(ALL、index、range、ref、eq_ref、
const(system)、NULL)
possible_keys :可能会应⽤的索引
key : 最终选择的索引
key_len :索引覆盖⻓度,主要是⽤来判断联合索引应⽤⻓度。
rows :需要扫描的⾏数
Extra :额外信息
4.type信息详解
4.1 ALL 没有使⽤到索引
a. 查询条件没建⽴索引
mysql> desc select * from city where district='shandong';
b. 有索引不⾛
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode!='CHN';
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode not in ('CHN','USA');
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode like '%CH%';
4.2 index全索引扫描
mysql> desc select countrycode from city;
4.3 range 索引范围扫描
会受到: B+TREE额外优化,叶⼦节点双向指针
mysql> desc select * from city where id<10;
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode like 'CH%';
以下两种查询,⼤⼏率受不到叶⼦节点双向指针优化。
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA';
建议: 如果查询列重复值少的话,我们建议改写为 union all desc
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' union all
select * from city where countrycode='USA';
4.4 ref 辅助索引等值查询
desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN';
4.5 eq_ref : 多表连接查询中,⾮驱动表的连接条件是主键或唯⼀键时
mysql> desc select city.name,country.name
from city
left join country
on city.countrycode=country.code where city.population<100;
4.6 const(system): 主键或唯⼀键等值查询
mysql> select * from city where id=1;
4.7 NULL
mysql> desc select * from city where id=1000000000000000;
5.key_len信息详解
5.1 作⽤
⽤来判断联合索引应⽤的部分。
例如:
idx(a,b,c)
我们希望应⽤联合索引的部分越多越好
5.2 如何计算
key_len=a+b+c
列的key_len⻓度,按照每列的最⼤预留⻓度来做的计算。
create table t1 (
id int,
a int ,
b char(10),
c varchar(10))
最⼤存储预留⻓度(字节):
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
--------
数据类型 : 占⽤字节量 有not null 没有Not Null
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
--------
数字类型:
tinyint : 1字节 1 1+1
int : 4字节 4 4+1
bigint : 8字节 8 8+1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
--------
字符串类型:
utf8:
char(10) : 10*3字节 =30 30 30+1
varchar(10) : 10*3+2字节=32 32 32+1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
--------
utf8mb4:
char(10) :10*4字节 =40 40 40+1
varchar(10) :10*4字节+2 =42 42 42+1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
--------
use test;
create table test (
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
a int not null , # 4
b int , # 5
c char(10) not null , # 40
d varchar(10), # 43
e varchar(10) not null # 42
)engine=innodb charset=utf8mb4;
alter table test add index idx(a,b,c,d,e);
5个列覆盖:
4+5+40+43+42=134
4个列覆盖:
4+5+40+43=92
3个列覆盖:
4+5+40=49
2个列覆盖:
4+5=9
应⽤1个列:
4
5.3 测试
mysql> desc select * from test where a=10 and b=10 and c='a' and d='a'
and e='a';
mysql> desc select * from test where a=10 and b=10 and c='a' and d='a';
mysql> desc select * from test where a=10 and b=10 and c='a';
mysql> desc select * from test where a=10 and b=10;
5.4 联合索引应⽤细节
条件:
联合索引应⽤要满⾜最左原则
a.建⽴联合索引时,选择重复值最少的列作为最左列。
b.使⽤联合索引时,查询条件中,必须包含最左列,才有可能应⽤到联合索引。
联合索引不同覆盖场景:
mysql> alter table t100w add index idx(num,k1,k2);
num : 5
k1 : 9
k2 : 17
a.全部覆盖 (key_len:31)
mysql> desc select * from t100w where num=913759 and k1='ej' and
k2='EFfg';
mysql> desc select * from t100w where k1='ej' and k2='EFfg' and
num=913759 ;
mysql> desc select * from t100w where num=913759 and k1='ej' and k2
in('EFfg','abcd');
mysql> desc select * from t100w where num=913759 and k1='ej' and k2
like 'EF%';
说明:
a= and b= and c=
b= and c= and a=
b.部分覆盖 idx(a,b,c)
where a = and b =
where b = and a =
where a =
where a = and b> < >= <= in like between and and c=
例如:
mysql> desc select * from t100w where num=913759 and k1>'zz' and
k2='EFfg';
总结:
如果联合索引中间出现了<>,between,like都会使得索引匹配截⽌于此。
如何优化?
(num,k1,k2) ----> (num,k2,k1)
mysql> desc select * from t100w where num=913759 and k2='EFfg' and
k1>'zz';
c. 完全不覆盖 idx(a,b,c)
where b c
where b
where c
6.extra 额外的信息
using filesort ---> group by \ order by \distinct \ union all
mysql> desc select * from city where countrycode='CHN' order by
population;
注意: where+order by⼀定要点联合索引
优化:
mysql> alter table city add index idx_1(CountryCode,population);
mysql> show index from city;
mysql> desc select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN' order by
population;
7.应⽤场景
数据库慢:
a. 应急性的慢。
show full processlist; ----> 慢语句 ----> explain SQL ---> 优化索引、改
写语句
b. 间歇性慢。
slowlog ----> 慢语句 ---> explain SQL ---> 优化索引、改写语句
第7章 建⽴索引的原则
1.说明
为了使索引的使⽤效率更⾼,在创建索引时,必须考虑在哪些字段上创建索引和创建什么类型的索引
2.降低索引树⾼度
(必须的) 建表时⼀定要有主键,⼀般是个⽆关⾃增列数字列。
3.选择唯⼀性索引
1.唯⼀性索引的值是唯⼀的,可以更快速的通过该索引来确定某条记录。
2.例如,学⽣表中学号是具有唯⼀性的字段。为该字段建⽴唯⼀性索引可以很快的确定某个学⽣的信息。
3.如果使⽤姓名的话,可能存在同名现象,从⽽降低查询速度
优化⽅案:
1.如果⾮得使⽤重复值较多的列作为查询条件(例如:男⼥),可以将表逻辑拆分
2.可以将此列和其他的查询类,做联和索引
select count(*) from world.city;
select count(distinct countrycode) from world.city;
select count(distinct countrycode,population ) from world.city;
4.尽量使⽤前缀来索引
如果索引字段的值很⻓,最好使⽤值的前缀来索引。
5.限制索引的数⽬
索引的数⽬不是越多越好。
可能会产⽣的问题:
1.每个索引都需要占⽤磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越⼤。
2.修改表时,对索引的重构和更新很麻烦。越多的索引,会使更新表变得很浪费时间。
3.优化器的负担会很重,有可能会影响到优化器的选择.
4.percona-toolkit中有个⼯具,专⻔分析索引是否有⽤
6.删除不再使⽤或很少使⽤的索引(percona toolkit)
1.表中的数据被⼤量更新,或者数据的使⽤⽅式被改变后,原有的⼀些索引可能不再需要。
2.数据库管理员应当定期找出这些索引,将它们删除,从⽽减少索引对更新操作的影响
7.建索引原则总结
1.必须要有主键,如果没有可以做为主键条件的列,创建⽆关列
2.经常做为where条件列 order by group by join on, distinct 的条件(业务:产品
功能+⽤户⾏为)
3.最好使⽤唯⼀值多的列作为索引,如果索引列重复值较多,可以考虑使⽤联合索引
4.列值⻓度较⻓的索引列,我们建议使⽤前缀索引.
5.降低索引条⽬,⼀⽅⾯不要创建没⽤索引,不常使⽤的索引清理,percona toolkit(xxxxx)
6.索引维护要避开业务繁忙期,建议⽤pt-osc
第8章 不⾛索引的情况
1.没有查询条件或者查询条件没有建⽴索引
select * from city;
select * from city where 1=1;
2.查询结果集是原表中的⼤部分数据,应该是15-25%以上
100w num 有索引
desc select * from t100w where num>1; ----> 全表
查询的结果集,超过了总数⾏数25%,优化器觉得就没有必要⾛索引了。
MySQL的预读功能有关。
可以通过精确查找范围,达到优化的效果。
1000000
desc select * from t100w where num>50000 and num<60000;
3.索引本身失效,统计信息不真实(过旧)
索引有⾃我维护的能⼒。
对于表内容变化⽐较频繁的情况下,有可能会出现索引失效。
⼀般是删除重建
现象:
有⼀条select语句平常查询时很快,突然有⼀天很慢,会是什么原因
select? --->索引失效,统计数据不真实
innodb_index_stats
innodb_table_stats
⽴即更新:
mysql> ANALYZE TABLE world.city;
4.查询条件使⽤函数在索引列上或者对索引列进⾏运算
错误的例⼦:select * from test where id-1=9;
正确的例⼦:select * from test where id=10;
算术运算
函数运算
⼦查询
5.隐式转换导致索引失效
这样会导致索引失效. 错误的例⼦:
mysql> CREATE TABLE `num` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` char(10) NOT NULL,
`num` char(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `inx` (`num`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4
mysql> desc num;
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | char(10) | NO | | NULL | |
| num | char(10) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
mysql> insert into num(name,num)
values
('z3','123456'),
('l4','123'),
('w5','321');
mysql> ALTER TABLE num ADD INDEX inx(num);
mysql> SHOW INDEX FROM num;
mysql> DESC SELECT * FROM num WHERE num='123456';
mysql> DESC SELECT * FROM num WHERE num=123456;
6. <>,not in 不⾛索引(辅助索引)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum <> '110';
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum NOT IN ('110','119');
mysql> select * from tab where telnum <> '1555555';
+------+------+---------+
| id | name | telnum |
+------+------+---------+
| 1 | a | 1333333 |
+------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tab where telnum <> '1555555';
单独的>,<,in 有可能⾛,也有可能不⾛,和结果集有关,尽量结合业务添加limit
or或in 可以修改成union all
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum IN ('110','119');
改写成:
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum='110'
UNION ALL
SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum='119'
7.like “%_” 百分号在最前⾯不⾛
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum LIKE '31%' ⾛range索引扫描
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM teltab WHERE telnum LIKE '%110' 不⾛索引
%linux%类的搜索需求,可以使⽤elasticsearch 或者 mongodb 专⻔做搜索服务的数据库产品

